Rural Water Supply
Public Health Engineering Department was created in 1956. The department is entrusted with the responsibility of providing safe drinking water and sanitation facilities in rural areas of Assam.
PHED carries out aforementioned activities in rural areas of Assam thorough-
Characteristics of SAFE WATER
What is Block?
A block is an administrative entity. The jurisdiction is generally limited to rural parts of a district. There is usually more than one block within a district.
What is Gram Panchayat?
Gram panchayats are local self-governments at the village in India. The gram panchayat is the foundation of the Panchayat System. A gram panchayat can be set up in villages with minimum population of 300. Sometimes two or more villages are clubbed together to form group-gram panchayat when the population of the individual villages is less than 300.
What is village?
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, usually larger than a habitation with the population ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand (sometimes tens of thousands). Historically, in India, villages were a usual form of community for societies that depend on agriculture for subsistence.
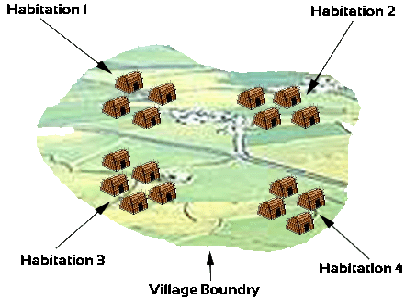
What is habitation?
It is a term used to define a group of families living in proximity to each other, within a village. It could have either heterogeneous or homogenous demographic pattern. There can be more than one habitation in a village but not vice versa.
What does Habitation Coverage status means?
Quality Affected Habitations (QA) - These are the habitations where water samples tested in laboratories have indicated levels of chemical contamination (limited to Arsenic, Fluoride, Iron, Nitrate and Salinity) higher than the permissible limits set by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS). Special focus is laid on monitoring of coverage status of such habitations under NRDWP.
| Chemicals | Permissible limit |
|---|---|
| Arsenic | 0.01 ppm |
| Fluoride | 1.5 ppm |
| Iron | 1 ppm |
| Nitrate | 45 ppm |
SC dominated habitations – SC dominated habitations are those habitations in which the Scheduled Caste population is equal to or more than 40% of total population.
ST dominated habitations – ST dominated habitations are those habitations in which the Scheduled Tribes population is equal to or more than 40% of total population.
This definition has been adopted by the Ministry of Drinking Water & Sanitation for purposes of monitoring theimplementation of NRDWP.
What is financial Year?
Spans the period from the 1st of April of a year to 31st March of the next year.
.g. 1/4/2016 to 31/3/2017 is the financial year 2016-17
What is Piped Water Supply scheme (PWSS)?
Such water supply systems provide water to various Delivery points away from the source of water through a pumping or gravity system and connections through pipelines.
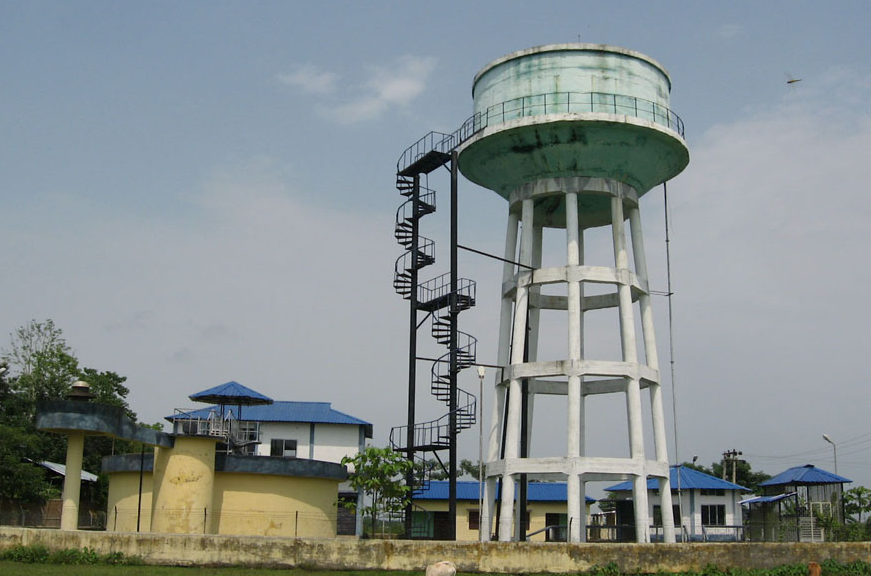


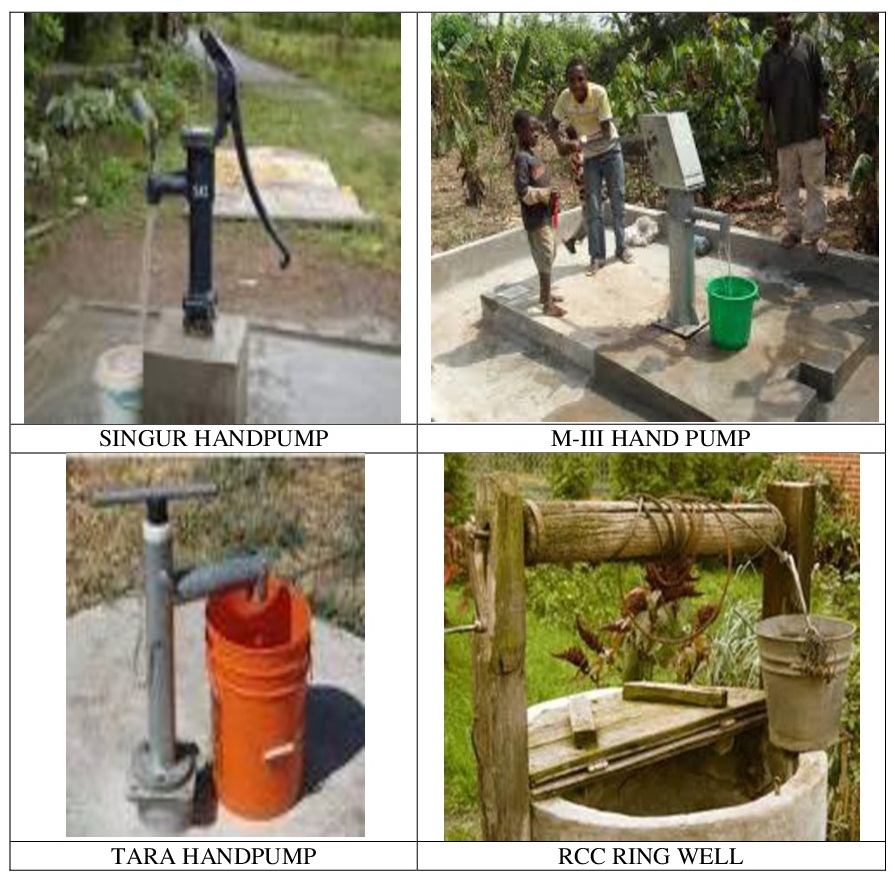
What is Spot Source?
Those water supply systems where the source of water and the supply/delivery system are both at the same point location, are called spot sources. Eg. Hand humps, wells, ponds etc.

National Rural Drinking Water Programme (NRDWP)
This programme was launched in April 2009 by the then Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation presently Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation, for assisting states in providing drinking water to the rural population of India. This programme has been emphasizing on water supply systems which are planned and managed by the community at the village level, for ensuring sustainable drinking water availability, convenient delivery systems and achieving water security at the household level.
Major Components of NRDWP (Renamed in April,2009)
Programme Activity may be sub-divided into:
Norms of Water Supply under NRDWP
Norms of providing water sources
